Concepts
Spinnaker is an open-source, multi-cloud continuous delivery platform that helps you release software changes with high velocity and confidence.
Spinnaker provides two core sets of features:
This article is an overview of these features:
Application management
You use Spinnaker’s application management features to view and manage your cloud resources.
Modern tech organizations operate collections of services—sometimes referred to as “applications” or “microservices.” A Spinnaker application models this concept.
Applications, clusters, and server groups are the key concepts Spinnaker uses to describe your services. Load balancers and firewalls describe how your services are exposed to users.
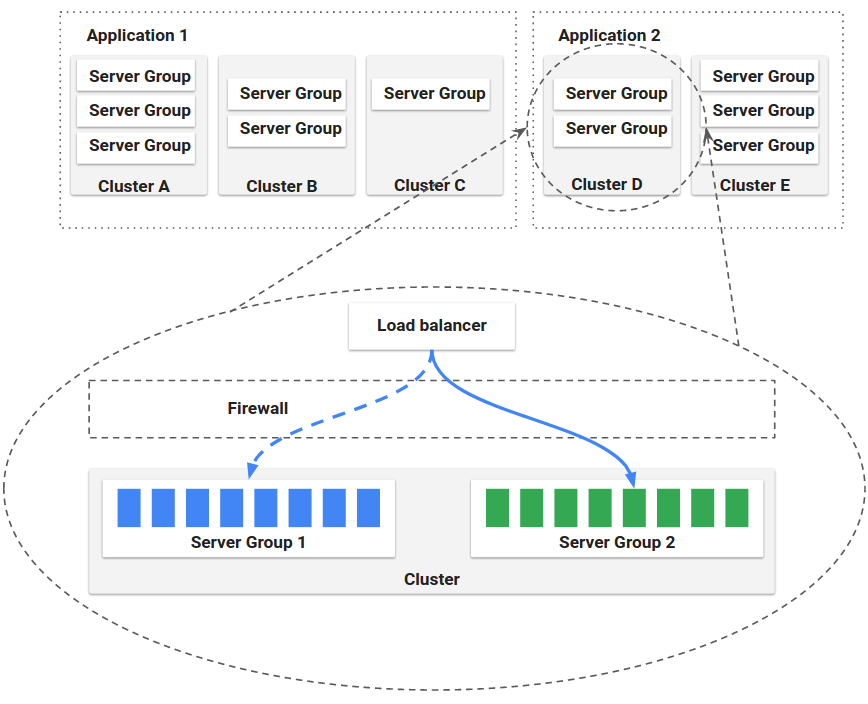
Application
An application in Spinnaker is a collection of clusters, which in turn are collections of server groups. The application also includes firewalls and load balancers.
An application represents the service which you are going to deploy using Spinnaker, all configuration for that service, and all the infrastructure on which it will run.
You will typically create a different application for each service, though Spinnaker does not enforce that.
Read more about applications, and how to create and configure them, here.
Cluster
You can define Clusters, which are logical groupings of Server Groups in Spinnaker.
Note: cluster, here, does not map to a Kubernetes cluster. It’s merely a collection of Server Groups, irrespective of any Kubernetes clusters that might be included in your underlying architecture.
Server Group
The base resource, the Server Group, identifies the deployable artifact (VM image, Docker image, source location) and basic configuration settings such as number of instances, autoscaling policies, metadata, etc. This resource is optionally associated with a Load Balancer and a Firewall. When deployed, a Server Group is a collection of instances of the running software (VM instances, Kubernetes pods).
Load Balancer
A Load Balancer is associated with an ingress protocol and port range. It balances traffic among instances in its Server Groups. Optionally, you can enable health checks for a load balancer, with flexibility to define health criteria and specify the health check endpoint.
Firewall
A Firewall defines network traffic access. It is effectively a set of firewall rules defined by an IP range (CIDR) along with a communication protocol (e.g., TCP) and port range.
Learn more about cluster management on the Clusters page.
Application deployment
You use Spinnaker’s application deployment features to construct and manage continuous delivery workflows.
Pipeline
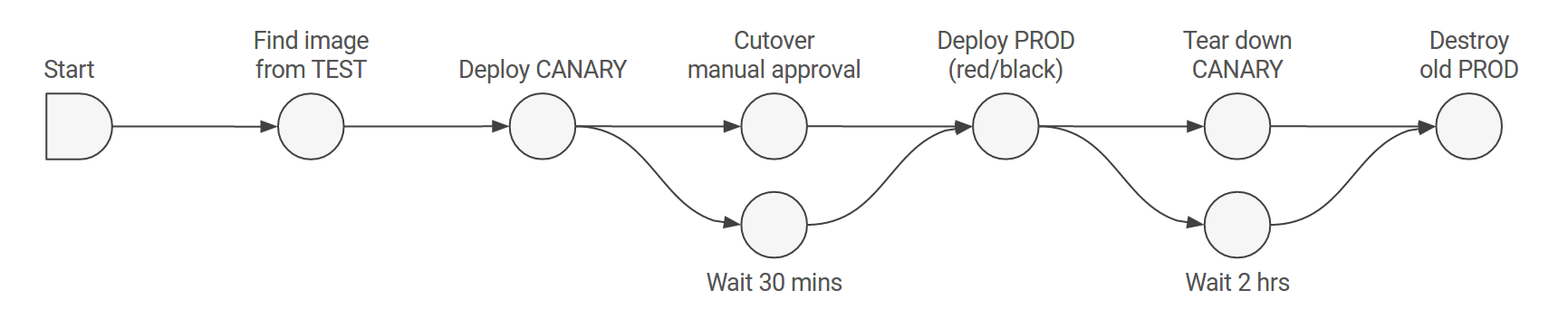
The pipeline is the key deployment management construct in Spinnaker. It consists of a sequence of actions, known as stages. You can pass parameters from stage to stage along the pipeline.
You can start a pipeline manually, or you can configure it to be automatically triggered by an event, such as a Jenkins job completing, a new Docker image appearing in your registry, a CRON schedule, or a stage in another pipeline.
You can configure the pipeline to emit notifications, by email, Slack, or SMS, to interested parties at various points during pipeline execution (such as on pipeline start/complete/fail).
Stage
A Stage in Spinnaker is an atomic building block for a pipeline, describing an action that the pipeline will perform. You can sequence stages in a Pipeline in any order, though some stage sequences may be more common than others. Spinnaker provides a number of stages such as Deploy, Resize, Disable, Manual Judgment, and many more. You can see the full list of stages and read about implementation details for each provider in the Reference section.
Deployment strategies
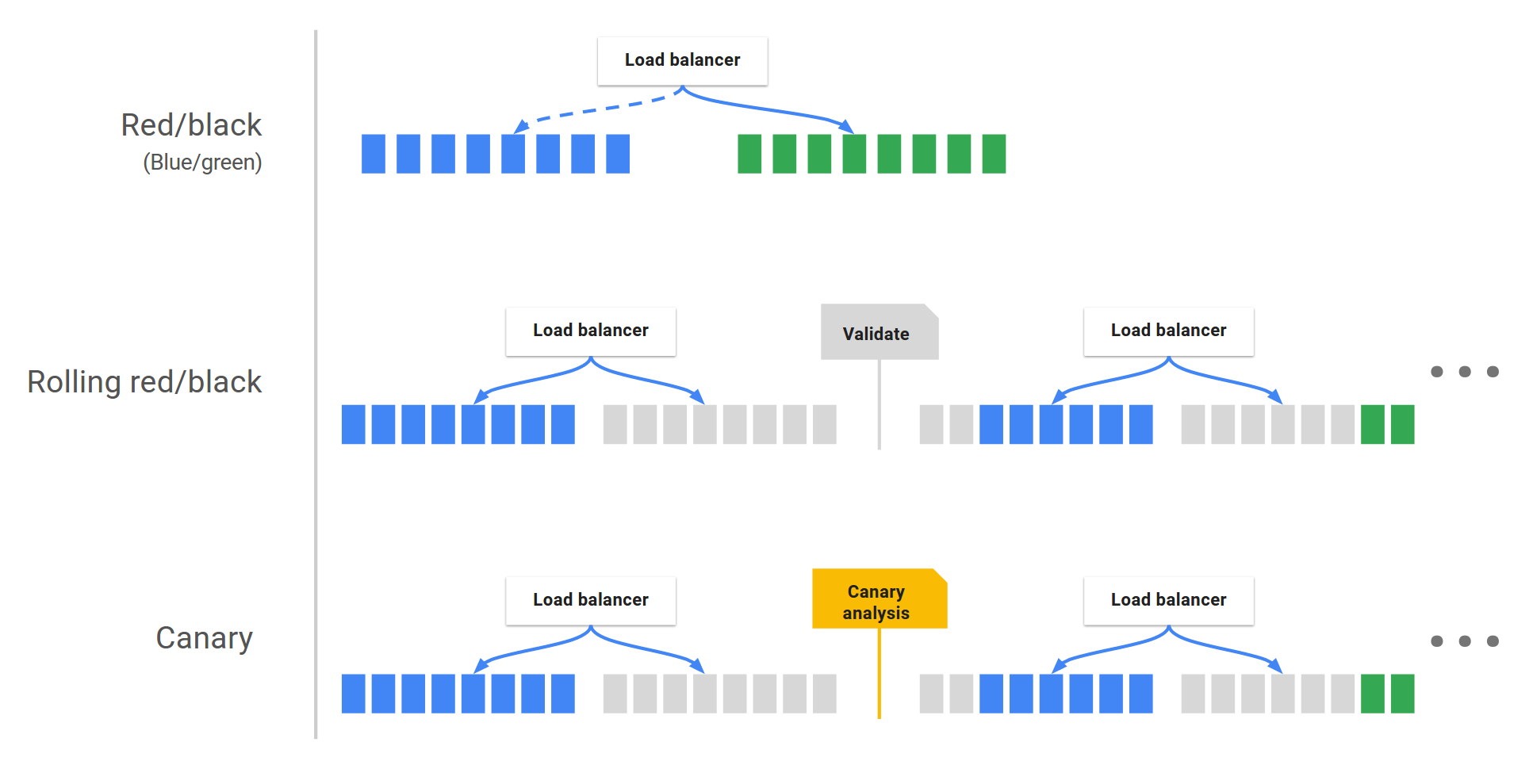
Spinnaker treats cloud-native deployment strategies as first class constructs, handling the underlying orchestration such as verifying health checks, disabling old server groups and enabling new server groups. Spinnaker supports the red/black (a.k.a. blue/green) strategy, with rolling red/black and canary strategies in active development.
Learn more about deployment management on the Pipelines page.